Understanding your credit score
Before you can improve your credit score, you must understand it: know how it is calculated and what it is used for.
Your credit score is a part of the package of information lenders use to decide whether or not they will lend you money or extend credit. Besides lenders, it’s used by stores, auto dealers, employers, and insurance companies. A higher score indicates to these people that you are fiscally responsible and that the risk of lending to you is low. It should result in lower interest rates, larger credit limits and better terms.
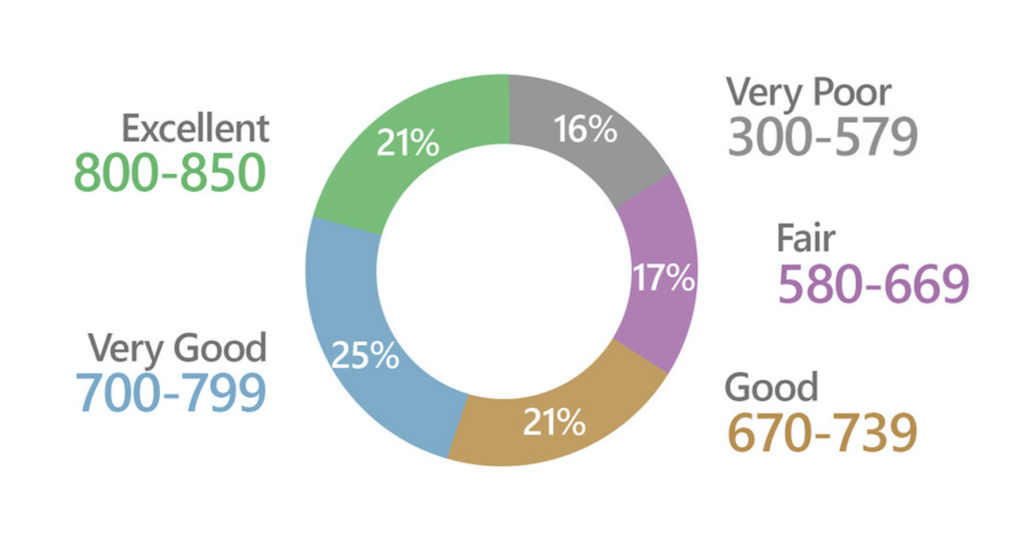
The primary credit scoring model you need to know about is FICO®. It’s used to determine your creditworthiness. That is, how likely you are to repay your loan. FICO® is a Data Analytics Company that uses the information received from the three major credit bureaus, Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax to determine and measure consumer credit risk. FICO® scores use a range of 300-850.
FICO® Score Ranges:
7 Ways to Increase your Credit Score
- Check your credit report – Dispute inaccuracies
- Some statistics say that as many as 60% of credit reports contain errors, so check your credit reports at least once a year.
- You can call and get your credit report for Free: 877-322-8228. They do not provide your credit score.
- You can go online and get your credit report for free from www.annualcreditreport.com. They do not provide your credit score.
- You can go online to www.myfico.com and get your Credit Score for free once a year.
- Banks such as Chase report if a client’s credit score is going up or down on their online banking app. Find out if your bank offers a similar service and if your credit score is going down, check out why.
- Pay bills on time – every time
- Your payment history is the biggest factor in determining you credit score, it’s imperative that you pay your bills on time. According to FICO®, one new past due payment can cause as much as a 180-point drop on your FICO® score depending on your credit history and the severity of the late payment.
- Build a Credit History
- If you start with NO credit history and NO credit score you can build one in 6 months. The best way it to get a “Secured Credit Card” which is basically a pre-paid credit card. No history is just as damaging as a bad one.
- Use both types of credit to establish your history: revolving (credit cards) and installment loans (mortgages and car loans).
- The older your credit profile is, the better the credit AGE and the higher the credit score. According to FICO®, 15% of your credit score is based on the age of the credit profile so keep the same credit cards and installment loans as long as possible. Don’t close old credit cards, even if you don’t plan to use them.
- Apply for Credit Carefully
- Avoid making too many credit applications in a short period of time
- Pay off Debt Quickly
- Pay off credit cards in full every month and reduce your loans as quickly as possible by making extra payments.
- Put bonus, tax refunds, and gifted monies to paying down debt
- Keep your Credit Card balance below 30% of available limit
- As much as 30% of your FICO® score is related to your credit card balance. You can improve your credit score by keeping the balance below 30%. Your credit score will be higher if you have three credit cards with the balance below 30% of a $1,000 limit, vs. one credit card with a balance of 90% of a $3,000 limit.
- Time heals all
- Large medical debt is one of the greatest reasons for charge offs, bankruptcies, and low credit scores. This is proof that “Bad things can happen to good people.” Time heals all, and with time you can improve any credit score. Most issues drop off your credit report within 7 years but may go faster if you work on it.
The fastest ways to increase your credit score is to reduce your credit balance on credit cards to below 30% of your credit limit, and to always pay your bills on time. Monitor your credit for mistakes monthly, and keep in mind the longer you keep the same revolving or installment credit lines, the higher your credit score will be. With a little effort and attention, you can be the boss of your financial future.

Recent Comments